Treatment of claw toes
Conservative treatment
At the stage of non-major and/or reducible deformations, modifications of the (more comfortable) shoes wearing are preferred. Pedicure care can be combined with the use of soles or orthoplasties (silicone elastomer orthotics, possibly tailor-made). Self-paced exercises can also be proposed to relax the muscles and tendons at the back of the leg and under the foot.
Surgical treatment
At a more advanced stage, surgical treatment is being considered. In addition to the treatment of the claw toes, the associated deformations responsible will be corrected, if necessary. Thus, the claw of the 2nd toe as part of a hallux valgus will also require treatment of the 1st radius. For a cavus foot, it has to be major.
The diversity of pathological situations and techniques makes it difficult to present a comprehensive presentation. We will remain schematic for greater clarity.
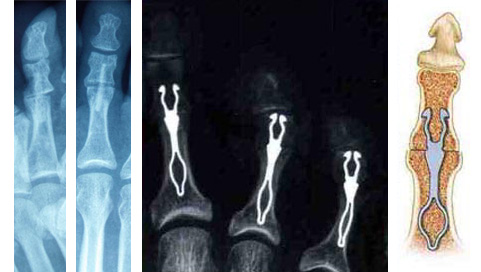
1 – The most common technique is to perform arthroplasty of the interphalangial joint of the toe. The distal part of the phalanx, at the origin of the painful conflict, is restored. Depending on the case, a transient pin may be installed to maintain the reduction. This creates a neo-articulation, correcting the claw while retaining some mobility.
It can be combined with tendon transfer (flexor tendon) or cut into percutaneous tendon (tenotomy) to better control claw correction.
2 – In some cases an inter-phalangial joint blockage is required. Fixation can be done without equipment. In some cases a pin will be put in the toe, and it will be removed in consultation 3 to 5 weeks later. Otherwise it is possible to put an internal implant.
3 – Finally, it may be justified to intervene on the metatarsal itself if the metatarso-phalangian joint would achieve a recoil of the toe. This can allow correction of the claw if it is reducible. The gesture is carried out with or without material, in percutaneous or open sky
The corns (or callus) will disappear gradually and spontaneously because of the removal of friction zones.
Surgical treatment results in prolonged swelling (edema) due to low lateral toe mobility. If you can do some percutaneous surgery, it doesn’t affect edema.
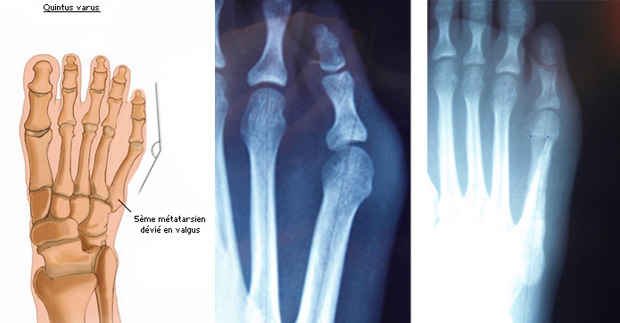
Special case of the 5th toe
There are two main lesions: Taylor’s Bunion with pain “in the tailor position” where the outside of the foot presses on the floor, the Quintus Varus or “bunionette” mirror lesion on the opposite side of the hallux valgus.
The claw of the fifth toe is treated with inter-phalangian arthroplasty (see above).
The outer bump of the head of the 5th metatarsal (quintus varus) is operated by an osteotomy (bone section) of the 5th metatarsal, sometimes associated with a gesture of skin plasty and an elongation of the extensor tendon.